Healthcare
Hospitals rely on EtO to sterilize medical instruments needed in patient care. EtO has the advantage of excellent material compatibility, though the cycle times are longer than other methods.
Medical Device Manufacturing
According to the FDA, over 50% of all medical devices used in the US are sterilized with EtO. EtO is a very effective sterilizing agent and offers excellent material compatibility and penetrating ability, allowing medical device sterilization companies to sterilize products by the pallet.

Supply Chain Logistics
Medical devices that are sterilized with EtO and then shipped may continue to off-gas for days. During transport, EtO accumulates in trucks and exposes workers who receive and unload shipments. Once in storage facilities, the off-gassing continues and accumulation of emissions can often exceed OSHA’s permissible exposure limit.
What Makes Ethylene Oxide Hazardous?
Despite its usefulness in these applications, EtO poses serious hazards and health risks. EtO is a highly flammable gas, which is explosive in air from 3% by volume to 100% by volume. While EtO is toxic and a primary irritant, the primary health concern is that EtO is a known human carcinogen which has been associated with an increase in several types of cancer including breast cancer and leukemia. EtO is also a mutagen and teratogen and has been associated with an increase in both miscarriages and birth defects. The EtO molecule is a strained three membered ring which can react with and damage DNA and other biologically important molecules.
Primarily because of carcinogenic properties of EtO, exposure limits and safety guidelines for using EtO in the workplace have been developed. OSHA has an EtO specific standard (29 CFR 1910.1047) and OSHA, the EPA and other government and non-government (e.g. AAMI) have produced standards and other guidance on the safe use of EtO.

Common Symptoms of Exposure
Exposure to EtO can occur from inhalation or direct contact. Exceeding exposure limits can cause:
- Cancer
- Nose and throat irritation that damages air passages and respiratory functions
- Damage to the cardiovascular system
- Chemical burns and frostbite to skin (contact with liquid EtO)
- Corneal burns and cataracts (contact with liquid EtO)
-
Increased risk of miscarriage and birth defects
Available Monitoring Solutions
If your facility uses EtO or is exposed to harmful off-gassing, a continuous monitoring system could save a life.

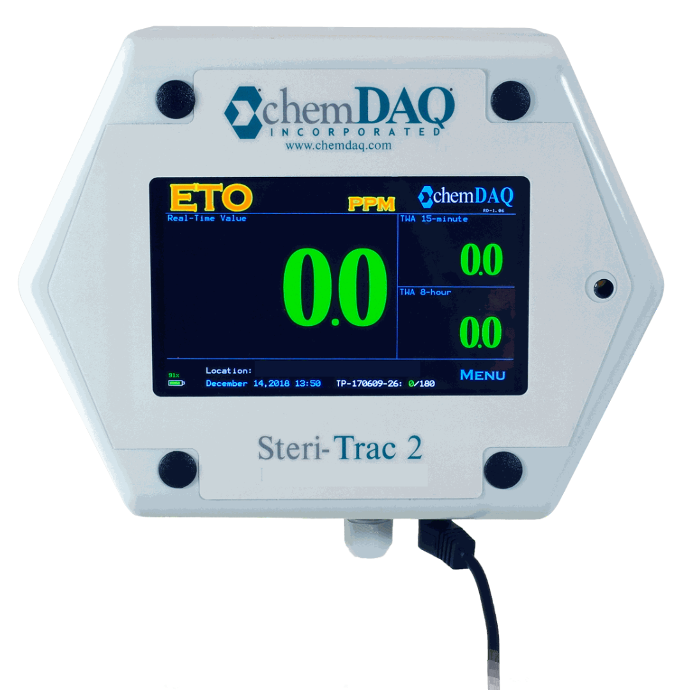
Steri-Trac® Sensor
EtO detection sensors are notorious for being sensitive to other gasses. ChemDAQ’s Steri-Trac Sensor features patented filter technology that prevents gasses, such as alcohols and carbon monoxide from interfering with accurate readings of EtO vapor. It can be used in intrinsically safe applications and is available for Oxygen and Lower Explosive Limit applications as well.
Steri-Trac® Series
ChemDAQ’s premier fixed area monitoring system, the Steri-Trac series of products are designed to continuously measure and alert you to hazardous vapor levels in the air.
Sensor Communication Interface (SCI™)
The SCI is a multi-configurable monitoring solution to accurately and reliably detect vapors throughout your facility and communicate readings to a compatible data system for enhanced connectivity.
Connect with a Product Expert
Need help determining which monitoring system best fits your needs? We can help!
Leading Brands Monitor for EtO